Whether in space or on Earth, conserving resources and reducing waste is the best practice to ensure sustainability. Every day, NASA strives to produce innovations in technology that are environmentally responsible without sacrificing effectiveness or efficiency. The following are NASA technologies ready for licensing for various environmental applications.
 Effective Wastewater Treatment Recovers Ammonia For Fertilizer
Effective Wastewater Treatment Recovers Ammonia For Fertilizer
Nitrogen pollution is a critical environmental issue that causes serious changes to aquatic ecosystems. Insufficient municipal water filtration processes allow nitrogen to seep into groundwater, and the typical ion-exchange resins usually used to treat ammonia are expensive and not as selective. NASA’s Ammonia Recovery System is a lower-cost solution that reduces ammonia concentrations in wastewater to less than 1 ppm. The ammonia captured can be recycled as an environmentally friendly fertilizer. This technology can be used in various water treatment systems and has a broad range of potential applications in numerous industries, particularly agricultural.
Lightweight, Freeze-Resistant Hydration System
High-altitude climbers face the risk of their drink bottles freezing and subsequently not getting enough fluid intake 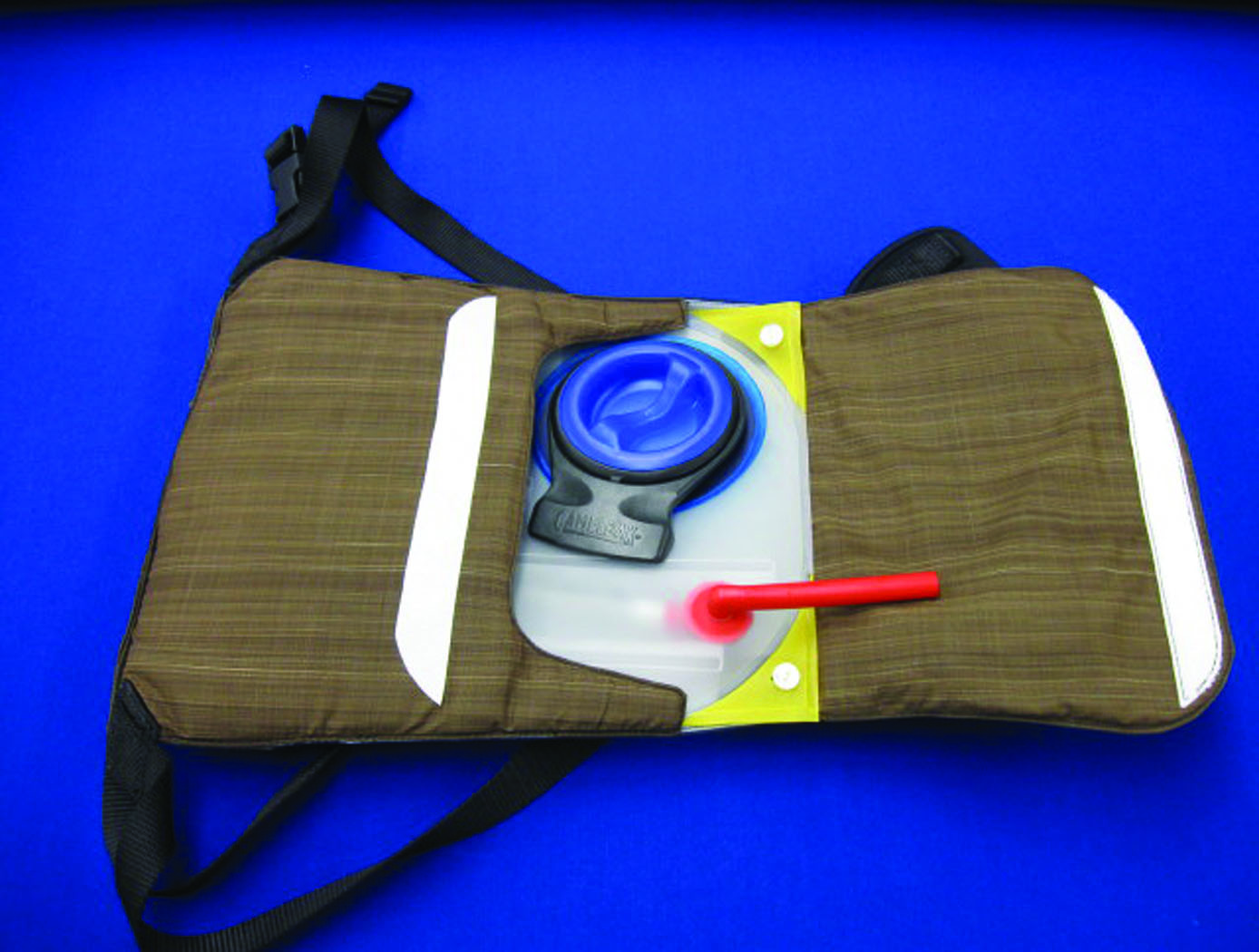 on their summit days, which poses a considerable health hazard. One astronaut-mountaineer conceived and designed the freeze-resistant hydration system to combat this. NASA’s Johnson Space Center is now offering the innovative Freeze-Resistant Hydration System for licensing, which prevents water from freezing in the container, tubing, and mouthpiece in even the harshest conditions on Earth. This technology can withstand minus 40 degrees Celsius and 15 mile-per-hour winds over a 12-hour summit day, and likely well beyond. The Freeze-Resistant Hydration System is well-suited for mountain climbers, cross-country skiers, snowmobilers, law enforcement, downhill skiers, and winter campers.
on their summit days, which poses a considerable health hazard. One astronaut-mountaineer conceived and designed the freeze-resistant hydration system to combat this. NASA’s Johnson Space Center is now offering the innovative Freeze-Resistant Hydration System for licensing, which prevents water from freezing in the container, tubing, and mouthpiece in even the harshest conditions on Earth. This technology can withstand minus 40 degrees Celsius and 15 mile-per-hour winds over a 12-hour summit day, and likely well beyond. The Freeze-Resistant Hydration System is well-suited for mountain climbers, cross-country skiers, snowmobilers, law enforcement, downhill skiers, and winter campers.
Robust, Low-Maintenance and Low-Cost Air Filtration
While HEPA filters can last for years without intervention,  pre-filtering systems that remove larger particles before they reach the HEPA filter need to be cleaned or replaced as often as once a week. This is a resource-intensive and expensive process, particularly in extreme temperatures or high-pressure environments.
pre-filtering systems that remove larger particles before they reach the HEPA filter need to be cleaned or replaced as often as once a week. This is a resource-intensive and expensive process, particularly in extreme temperatures or high-pressure environments.
NASA’s Glenn Research Center has developed a Multi-Stage Filtration System to collect a wide range of particle sizes and cleanse them through a unique feed system. The technology reduces the need to replace more sensitive and expensive filters by extending their working life. This technology sees applications in HEPA filters, fluid and gas dynamic research, air and gas systems, microgravity environments, fluid mechanics, commercial aircraft, submarines, and remote instruments.
To browse NASA's entire portfolio, please click here.
Follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook to stay up-to-date on our latest technology offerings.


